Hello World in Java
In the previous tutorial, you learned how to install Java on your computer. Now, let’s write your first Java program: “Hello, World”.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello, World!");
}
}
The above program prints Hello, World! on the screen.
Output
Hello, World!
Congratulations! You’ve just written your very first program. Keep coding! Now, let’s understand the code that you have just written.
Basic Structure of a Java Program
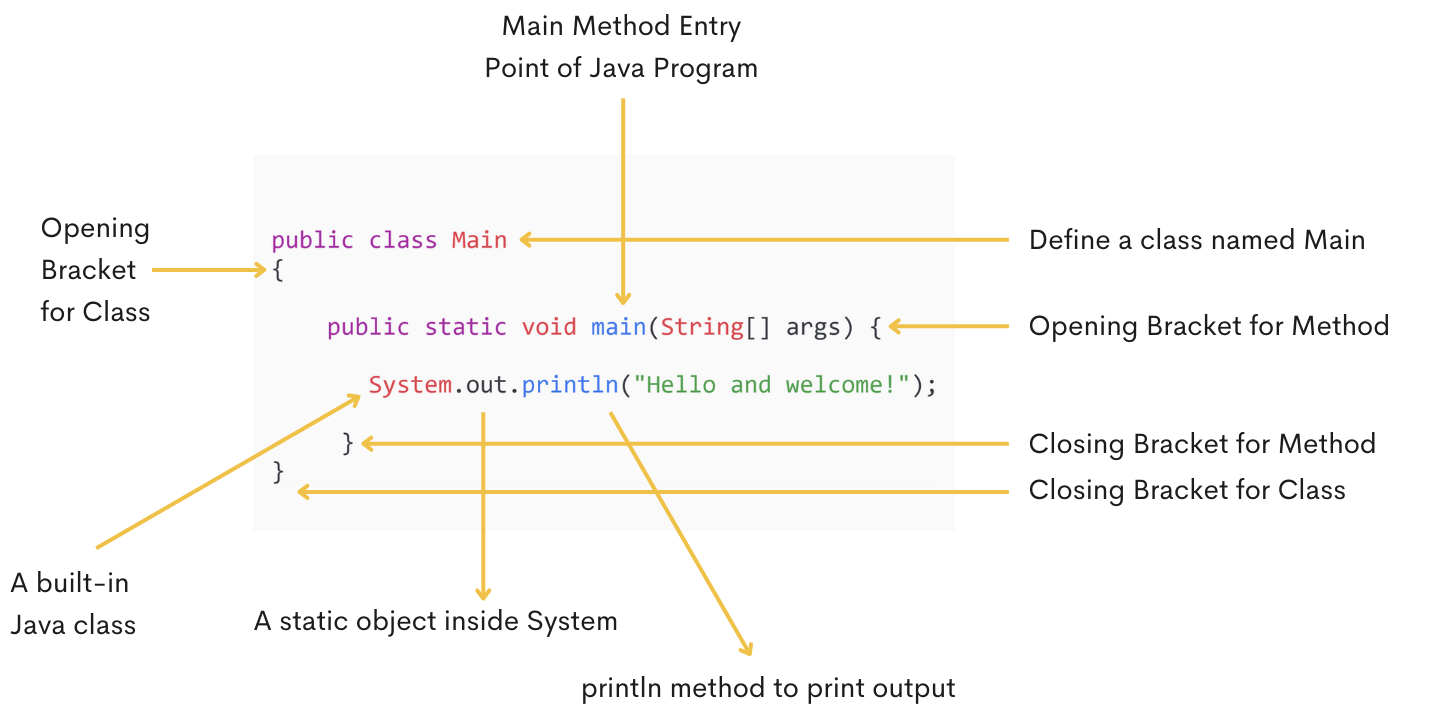
1. public class main (Class Definition)
Every Java program must have at least one class. The class keyword is used to define a class in Java, and Main is the name of the class. The public keyword in Java is an access modifier. We will learn more about access modifiers later in the upcoming tutorials.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Code Goes Here
}
}
2. main Method in Java
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
- public: Allows the method to be accessed from anywhere.
- static: A method can run without creating an object.
- void: It’s a return type that means a method is not returning anything.
- main: main is the name of the method.
- String[] args: Arguments of the method.
3. System.out.println()
System.out.println("Hello, World");
- System: Built in class.
- out: out is a static object inside the System class.
- println(): The println() method prints output to the console and moves to the next line.
How Java Executes Program
Java programs execute in two steps: first is compilation, and second is execution.
- Compilation(source code to byte code).
- Execution(byte code to native code).
1. Compilation
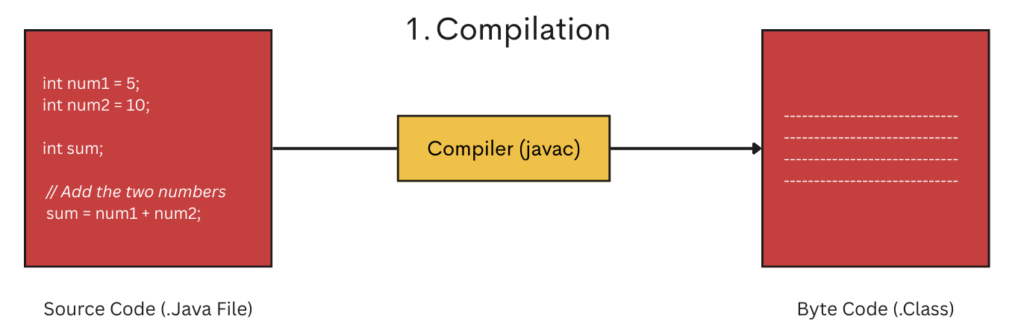
The Java compiler is a development tool included in the JDK(Java Development Kit) that converts Java source code into bytecode.

2. Execution
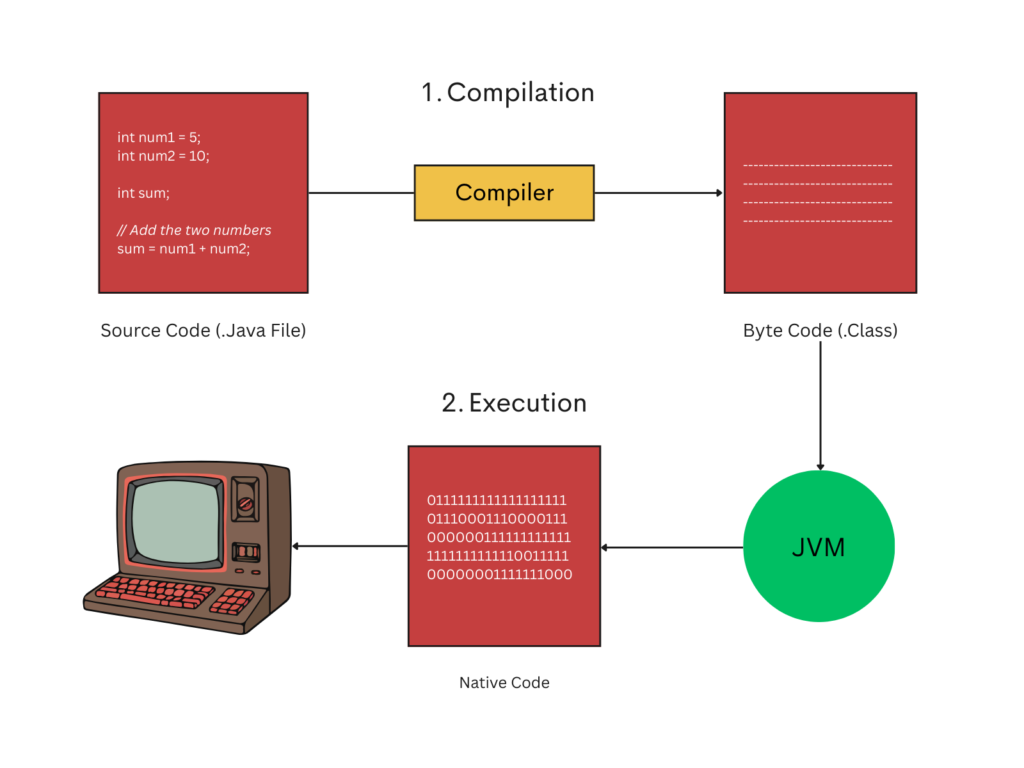
JVM(Java Virtual Machine) is part of JRE(Java Runtime), and JRE is part of JDK(Java Development Kit).

JVM(Java Virtual Machine) is part of JRE(Java Runtime), and JRE is part of JDK(Java Development Kit).
In the next tutorial, we’ll learn about comments in Java and how they help make code more readable and easier to understand.
Conclusion
Congratulations! You’ve successfully written and understood your first Java program, the classic Hello World example.
This small program might look simple, but it introduces you to some of the most important building blocks of Java, such as the main method, class structure, and how Java executes code. Every professional Java developer started their journey right here.
From this point forward, you can begin exploring:
- Variables and data types
- Conditional statements
- Loops
- Object-Oriented Programming concepts
At VairagiCodes, our goal is to make programming easy, practical, and beginner-friendly. Keep practicing, experiment with the code, and don’t be afraid to make mistakes, that’s how real learning happens.
Next Step: Try modifying the message inside System.out.println() or write multiple print statements to strengthen your understanding.
In the next tutorial, we’ll explore comments in Java, an essential concept that helps you write clear, readable, and well-documented code.
Java Tutorials
Stay Connected
Follow me on Instagram for Java tips, coding reels, and much more.
Subscribe to my YouTube Channel for learning the art of programming.