Variables in Java
In the previous tutorial, you learnt about comments in Java.
In this tutorial, you’ll learn what variables are in Java, how they work, why we need them, naming conventions, how variables are represented in memory, best practices, and real-world usage, all explained in a simple and practical way.
What is Variable in Java?
A variable is like a container that stores data. Each variable should be given a unique name.
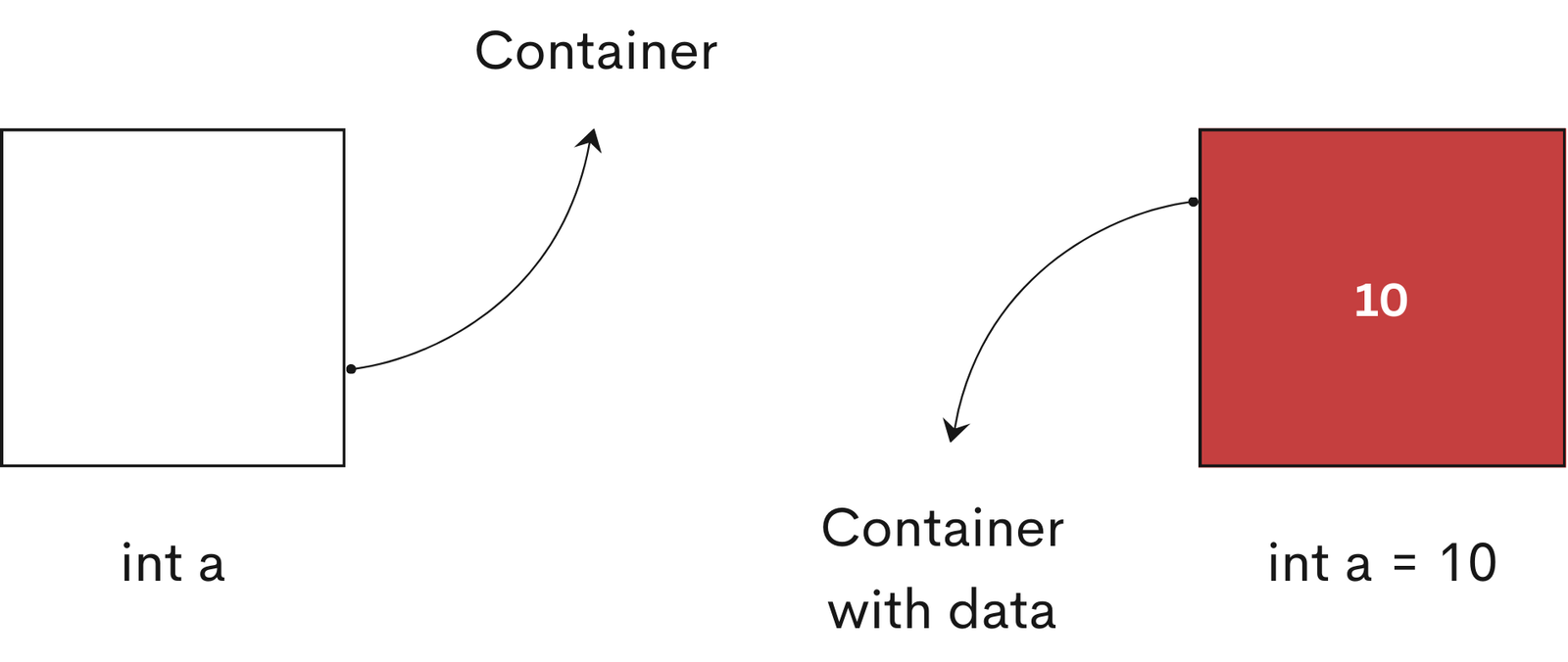
At any point during a program, you can access these containers (variables in Java) and access the data and you can also change it or use it to do something.
public class VariableInJava {
public static void main(String[] args) {
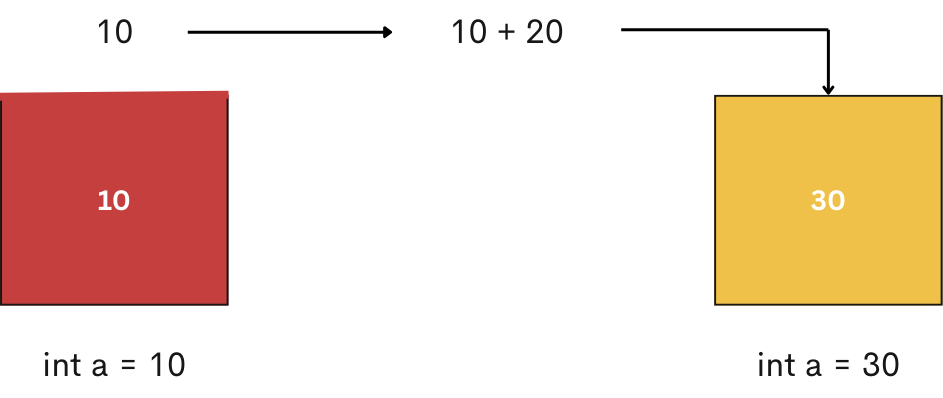
int a = 10;
a = a + 20;
System.out.println(a);
}
}
How can we use variables in Java programs?
In Java, using a variable starts with declaring it. Once declared, we can assign a value to the variable either immediately or at a later point in the program.
Using a variable in Java involves two main steps:
- Declaration
- Initialization
1. Declaration
In Java, a variable must be declared before it can be used in a program.
Syntax for declaring a variable in Java:
dataType variableName;
Example
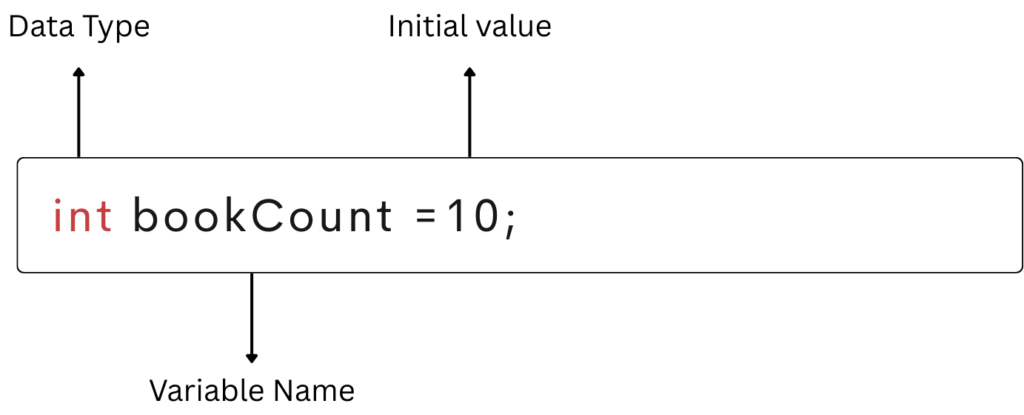
int bookCount;
In the above example, int is a data type in Java. A data type determines the kind of data a variable can store. We will explore data types in detail in an upcoming tutorial; for now, you only need to remember the basic syntax for declaring a variable in Java.
bookCount is the name of the variable. Every variable must be given a unique name, also known as an identifier.

Local variables must be initialized before use. Otherwise, Java will throw a compile-time error.
int bookCount;
System.out.println(bookCount); // compile-time error
2. Initialization
dataType variableName = initialValue;
(initialValue is optional at the time of declaration.)
Example
int bookCount = 10;
int bookCount;
bookCount = 10;
Note:
Java is a statically-typed language, which means you must declare the type of value a variable can hold before you use it.
int bookCount = 10;
bookCount = "Musafir Cafe"; // error: incompatible types
This causes a compile-time error because bookCount is an int, and Java does not allow changing a variable’s data type.
Updating the variable
The value of a variable can be changed or can be updated in the program, That’s why it is called a variable.
For example:
// initially, the person has 10 books
int bookCount = 10;
//now the person bought 10 more books
bookCount = bookCount + 10; //updating the initial bookCount
Naming convention for variables in Java
1. Java is case-sensitive: Hence, bookCount and BOOKCOUNT are two different variables.
For example:
int bookCount = 10;
int BOOKCOUNT = 30;
System.out.println(bookCount); // prints 10
System.out.println(BOOKCOUNT); // prints 30
2. Variables must start with either a letter, an underscore(_), or a dollar ($) sign.
For example:
int bookCount; // valid name and good practice
int _bookCount; // valid but bad practice
int $bookCount; // valid but bad practice
3. Variable names cannot start with numbers.
For example:
int 10Books; // invalid variable name
4. Variable names can’t use whitespace.
For example:
int book count; // invalid: whitespace is not allowed in variable names
5. When creating variables, choose a name that makes sense. For example, age, userName, and userEmail make more sense than variable names such as a, u, and e.
6. For one-word variable names, use all lowercase letters. For example, it is better to use book rather than a BOOK or Book.
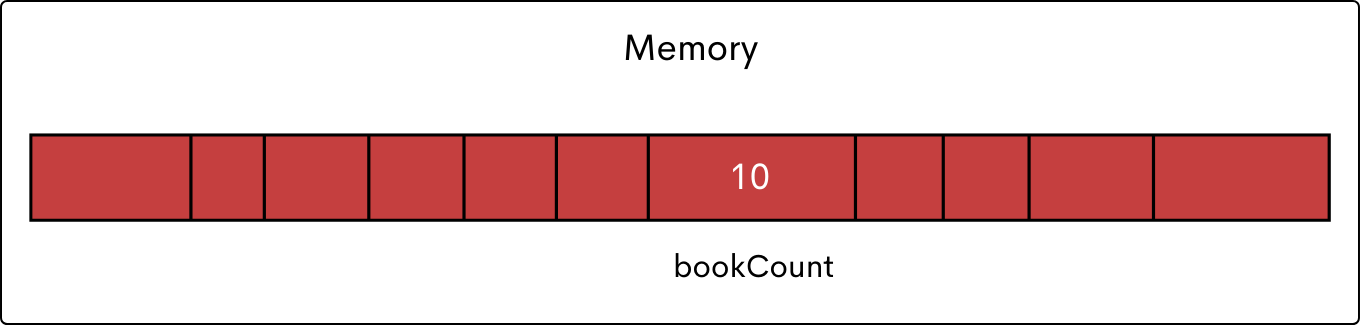
Variable representation in memory
Summary
Let’s quickly recap:
- Variables store data in Java programs.
- Every variable must be declared before use.
- Variables can be initialized during declaration or later.
- Java follows strict naming rules for variables.
- Understanding variables is essential for writing clean and maintainable code.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a variable in Java?
A variable in Java is a named memory location used to store data during program execution. Each variable has a data type that defines what kind of value it can store, such as int, float, or String.
Why do we use variables in Java?
Variables are used to store, update, and reuse data in a program. Without variables, programs would be limited to fixed values and would not be able to perform dynamic operations like calculations, user input handling, or data processing.
How do you declare a variable in Java?
A variable in Java is declared by specifying its data type followed by the variable name.
Example: int bookCount;
This tells Java that bookCount is a variable that can store integer values.
How do you initialize a variable in Java?
int bookCount = 10;
Initialization means assigning a value to a variable. You can also initialize a variable later in the program, but it must be initialized before use.
Can a variable be used without initialization in Java?
No. Local variables must be initialized before use. If you try to use an uninitialized local variable, Java will throw a compile-time error.
Example:
int bookCount;
System.out.println(bookCount); // compile-time error
Can we change the data type of a variable in Java?
No. Java is a statically typed language, which means once a variable is declared with a data type, its type cannot be changed.
Example:
int bookCount = 10;
bookCount = "Musafir Cafe"; // compile-time error
What is variable representation in memory?
When a variable is created, Java assigns a memory location to store its value. The variable name acts as a reference to that memory location, allowing the program to access and modify the stored data.
What’s Next?
Now that you understand variables in Java, the next step is to learn data types in Java.
In the next tutorial, we’ll learn about data types.
Java Tutorials
Stay Connected
Follow on Instagram for Java tips, coding reels, and much more.
Subscribe to VairagiCodes YouTube Channel for learning the art of programming.